September 13, 2024
Quantity Surveying: Over the Years
Author: Rhianyth Bater
Date: September 13, 2024
Categories:
Industry
Quantity surveying, and the practice of measuring, calculating, and costing construction projects, is a complex profession. Its roots can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where builders and architects relied on accurate measurements and calculations to ensure the success of their projects. So how far back does it go?
Ancient Egypt (3100 BCE - 30 BCE)

The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus – The British Museum
While the term "quantity surveying" didn't exist back then, the Egyptians certainly employed methods of measuring and calculating for their monumental construction projects. The Rhind Papyrus, a mathematical text from the 16th century BCE, includes problems related to calculating volumes of granaries and areas of fields. These calculations were essential for planning and executing large-scale construction projects. ‘Measurer of Royal Works’ and ‘Rope Stretchers’ were references to surveying roles for various projects at the time. Surveying tools that the Ancient Egyptians used were simple but effective. The most basic tools were used such as the plumb bob, cubit rods for short measurements and a calibrated rope of 100 cubits for longer measurements.
Biblical Times (c. 1000 BCE - 100 CE)
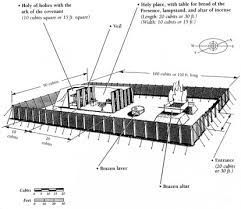
- Exodus 25-31: Describes the construction of the Tabernacle, including detailed specifications for its materials and dimensions.
- Luke 14:28-30 New King James Version (NKJV) “For which of you, intending to build a tower, does not sit down first and count the cost, whether he has enough to finish it— lest, after he has laid the foundation, and is not able to finish, all who see it begin to mock him, saying, ‘This man began to build and was not able to finish’?”
Ancient Rome (c. 753 BCE - 476 CE)
Vitruvius' writings provide valuable insights into the architectural practices of the Romans. He discusses the importance of precise measurements and calculations in architectural design, including the use of the "module" as a unit of measurement.
Medieval Europe (c. 500 CE - 1500 CE)
Medieval builders often used a system of "foot" and "yard" measurements. They also employed techniques such as "cubing" to estimate the volume and cost of materials needed for construction projects. The construction of cathedrals, with their intricate stonework and stained glass, required careful planning and precise measurements.

The Renaissance (c. 1400 - 1600)
Renaissance architects like Leonardo da Vinci and Filippo Brunelleschi used more advanced mathematical techniques and instruments for measuring and calculating. The development of perspective drawing, and the use of scale models, also contributed to the refinement of quantity surveying practices.
The 17th and 18th Centuries: Early Modern Period
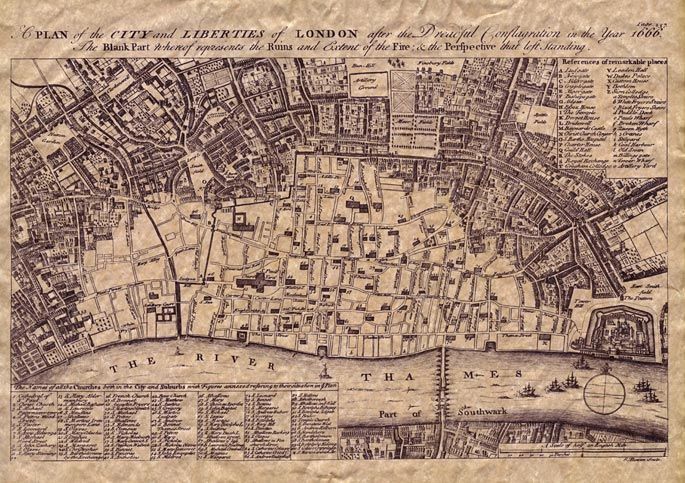
During this period, architects and engineers continued to refine their methods for measuring and calculating construction projects. The development of more accurate surveying instruments and the use of mathematical tables facilitated more precise calculations.Following the Great Fire of London in 1666, Dr Robert Hooke was assigned the role of Surveyor to the City of London and Chief Assistant to Sir Christopher Wren to help rebuild London.
The 19th Century: Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in the construction industry, including the development of new materials, technologies, and methods. Quantity surveying became increasingly important as large-scale infrastructure projects, such as railways and factories, were undertaken. The emergence of specialised engineering firms and the standardisation of building practices contributed to the development of the profession and the birth of BoQs
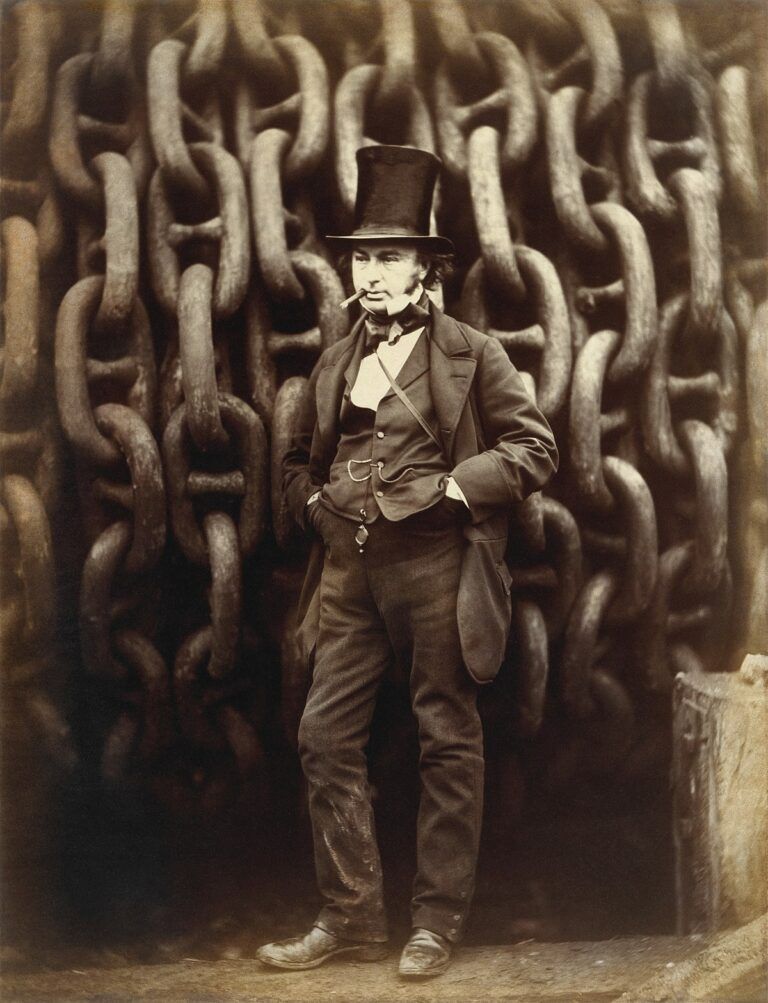
In 1833 Bristol Railway Committee engaged Isambard Kingdom-Brunel to survey a railway line between Bristol and London, he presented his proposals to the Committee after only three months. It was an ambitious scheme with carefully planned gradients to make the route as level and straight as possible to promote high-speed travel on the line. The Great Western Railway Act was approved by Parliament in 1835 and work on the 116-mile line started in 1836.
The 1800's also saw the establishment of professional bodies dedicated to quantity surveying, such as RICS (UK) who appointed their first president in 1869. These organisations play a crucial role in promoting the development of the profession, setting standards, and providing training and education for quantity surveyors.
The 20th Century: Modern Quantity Surveying
- The rise of computer-aided design (CAD) and building information modelling (BIM): These technologies have revolutionised the way quantity surveyors work, enabling more efficient and accurate measurement and cost estimation.

- The increasing complexity of construction projects: As projects have become more complex, quantity surveyors have had to adapt their skills and knowledge to meet the demands of the modern construction industry.
- The growing importance of sustainability and environmental considerations: Quantity surveyors now play a key role in assessing the environmental impact of construction projects and ensuring that sustainable practices are adopted.
Today, quantity surveying remains an essential profession, with quantity surveyors playing a vital role in the planning, design, and construction of buildings and infrastructure projects globally. The continued development of new technologies and the increasing complexity of construction projects will continue to shape the future of the profession.



